Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Hertz’s Observations during Experiments of Electromagnetic Waves,Hallwachs’ and Lenard’s Observations,Threshold Frequency for Photoelectric Effect, etc.
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5 V. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be:
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted would be
The maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is 3 eV. Its stopping potential is:
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation in terms of the stopping potential and the threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material is
The photoelectrons emitted from the surface of a certain metal by light of frequency are fully retarded by a reverse potential of and those ejected by light of frequency by a reverse potential of . The value of Planck's constant as calculated from above information is
The work functions of Caesium , Potassium and Sodium are respectively. If incident electromagnetic radiation has an incident energy of , which of these photosensitive surfaces may emit photoelectrons?
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : Out of microwaves, infrared rays and ultraviolet rays, ultraviolet rays are the most effective for the emission of electrons from a metallic surface
Statement II : Above the threshold frequency, the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons is inversely proportional to the frequency of the incident light
In the light of above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
The variation of stopping potential as a function of the frequency of the incident light for a metal is shown in figure. The work function of the surface is
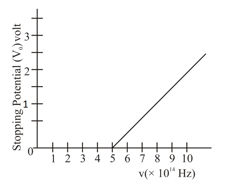
A metallic surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential is . If the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential becomes . The threshold wavelength for this metallic surface will be
The work functions of Aluminium and Gold are and respectively. The ratio of the slope of the stopping potential versus frequency plot for Gold to that of Aluminium is
The work function for two metals are and . Find the approximate difference between their threshold wavelength.
(use )
Based on given graph between stopping potential and frequency of irradiation, work function of metal is equal to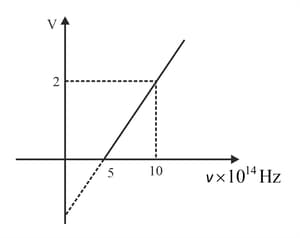
In the photoelectric experiment apparatus containing the collector and the emitter plate, a saturated photoelectron current is observed. If an external electric field is applied in the direction opposite to the motion of the photoelectrons, what is the change observed in each of the following? Give reasons.
i. The saturation value of the photocurrent,
ii. The kinetic energy of the photoelectrons striking the collector plate
Give reason for the following observation-
A radiation of wavelength incident on a metal sphere placed on an insulated stand results in the emission of photoelectrons for some time and then stops.
Increase in the frequency of the incident radiations increases the
A gas molecule absorbs a photon of wavelength and releases two photons one of which has wavelength . Find the wavelength of other photon.
In a photoelectric effect, the maximum energy of the photoelectron is attained with exposure of light. If the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron is , the threshold wavelength will be (use )
A light source is emititing radiations of wavelengthrs and if the light source strikes a metal surface having work function . Calculate the total number of photoelectrons emitted per second and charge per second if power is equally distributed.
Threshold frequency of incident radiation in a photoelectric experiment
A) depends on material
B) depends on wavelength
C) depends on intensity
